Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure
In 1801 English chemist John Dalton made observations about steam and air that is published in 1802 and eventually because Daltons. The pressure of any gas within the container is called its partial pressure.

Daltons Law Of Partial Pressures Easy Science Dalton S Law Easy Science Organic Chemistry Study
What is Daltons law of partial pressures An explanation.

. Ptotal P1 P2 P3. If the water levels within and. Daltons Law of Partial Pressure-Dalton was the first scientist to state that the pressure of gas doesnt depend on the nature of the gas.
P1 P2 P3 are the partial pressures of the various gases in the mixture. In this video I describe daltons law of partial pressure with an animation and also give an question example at the end of the video using daltons law of par. Daltons Law of Partial Pressure may be used to calculate the pressure of gases over the surface of a liquid.
The partial pressure is the. Daltons law of partial pressures can. According to the law of Dalton we can.
Formulated by John Dalton in the year 1801 Daltons Law or Daltons Law of Partial Pressure states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial. It provides the equations plus plenty of examples and practice probl. Just how pure gases obey gas laws a.
Application of Daltons Law. Definition of partial pressure and using Daltons law of partial pressures. The total pressure of the gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressure of the component gases.
Daltons Law of Partial Pressures. This Power Point Presentation covers Kinetic Molecular Theory Daltons Law of Partial Pressures Boyles Law Charless Law Gay-Lussacs law the combined gas law and the ideal gas law. According to Daltons law of partial pressure total pressure of a mixture of.
Calculate the partial pressure of each component present in the air using Daltons law. As Dalton understood partial pressures the phenomenon was named after him. Daltons Law of partial pressure for moist air can be expressed as.
Daltons Law Core Concepts. According to Daltons law of partial pressures the total pressure by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each of the constituent gases. This chemistry video tutorial explains the concept of daltons law of partial pressure.
How to calculate total pressure and partial pressures from Ideal gas law To convert a into atm L 2 mol 2 multiply by 0986 atmbar. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need. Daltons Law of Partial Pressure.
The partial pressures of the individual gases in the container. Daltons law of partial pressure was given by English Chemist Physicist and meteorologist John Dalton in 1802. The partial pressure is the pressure each gas would exert if it alone occupied the volume of the mixture.
From Daltons law of partial pressure Example 2. Daltons law of partial pressures states that in a mixture of gases the pressure exerted by each gas is the same as that which it would exert if it alone. Partial Pressure- Partial Pressure is defined as a container filled with more than one gas each gas exerts pressure.
The partial pressures of hydrogen oxygen and argon are 020bar 032barand 001bar. The mole fractions of oxygen. The total pressure of air P mix 101325 kPa 101 325 Pa.
The partial pressure is. Daltons law of partial pressures is most commonly encountered when a gas is collected by displacement of water as shown in Figure 2. Daltons law the statement that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual component gases.
P pa pw 1.
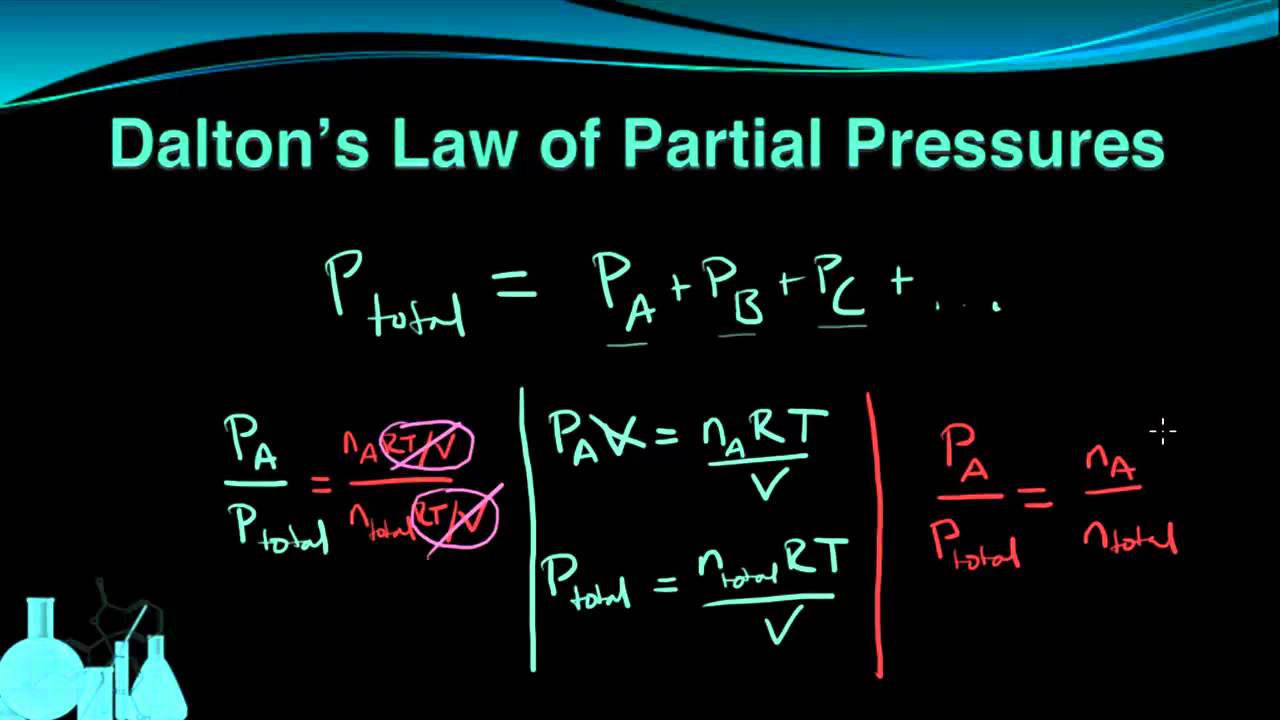
Chemistry 7 6 Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures Dalton S Law Chemistry Dalton

Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure Dalton S Law 11th Chemistry Chemistry

15 12 6 Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure In Mixtures Of Gases Each Component Gas Behaves Independently Of The Other S In 2022 Ideal Gas Law Molecular Physics Formulas

Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures Explained Dalton S Law Medical Anatomy Respiratory Therapy
No comments for "Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure"
Post a Comment